
Students can refer to this article for practicing questions. The explanations of the MCQs are also given. The above article provides solved MCQs on Meiosis. Call the step of prophase I when synaptonemal complex dissolves when chromatids are transparent and tetrads are considered bivalents? In metaphase I, the centromeres undergo division.ĥ. Meiosis is of evolutionary significance as it produces _?Ĥ.

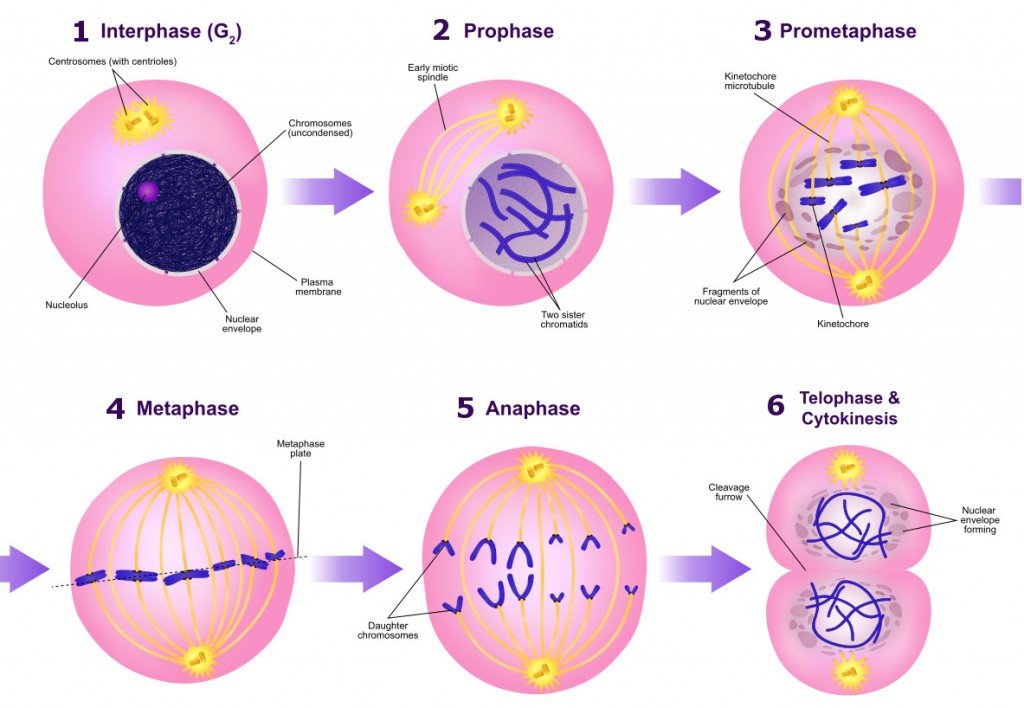
During meiosis, chromatids of individual chromosomes separate during _?ģ. prophase (pro metaphase) Chromosomes are duplex structures (2) Prophase, Metaphase.


Chiasmata is a spot where paired chromosomes stay in contact during the first meiosis metaphase.Ģ. Chiasmata formation takes place during _Įxplanation: The formation of chiasmata takes place during prophase I, and chromosomes are duplicated during this period. Textbook solution for Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology 5th edition 5th Edition Dicket Chapter 8 Problem 16PS. During metaphase, the chromosome organizes itself in the middle of the cell.ġ0. There are chromosomes arranged along the equator _Įxplanation: Metaphase is the 2nd level of cell division. Colchicine can cause polyploidy, artificially.ĩ. Polyploidy may be induced artificially by_Įxplanation: Polyploidy’s condition where diploid cells normally get one or more extra sets of chromosomes. Colchicine arrests metaphase for the stage of the division of cells.Įxplanation: Cytokinesis is a process of cell division that divides the cytoplasm of a parental cell into two daughter cells.Ĩ. Colchicine arrests which of the following stages of cell division?Įxplanation: Colchicine is an alkaloid in its natural state. The S phase is characterized by biosynthetic activity such as duplication of DNA and centrioles.Ħ. It is divided into the G1, S phase, and G2 phase. Replication of centriole occurs in _Įxplanation: Interphase is the longest phase of the cell cycle in which typical cells submit most of their lives. During this point, chromosomes move away from each other towards opposite spindle poles.ĥ. Tubulin is a Globular Protein It helps in dividing cells.Įxplanation: The 3rd stage of cell division is anaphase. Microtubules are polymers of alpha- and beta-tubulin dimers. Spindle fibers are formed by_Įxplanation: Spindle fibers are made up of microtubules. Synapsis facilitates the exchange of genetic material between the chromosomes.ģ. Bivalents are seen as shaping the synaptonemal complexes. RNA and protein synthesis occurs in Phase G1.Įxplanation: Zygotene is the second stage of the Meiosis prophase. It is an integral part of the Interphase. The RNA and protein synthesis occurs in_Įxplanation: The first phase of the cell cycle is phase G1.
#Prophase anaphase metaphase telophase download#
These are divided between the first division of the cell (meiosis I) and the second division thereof (meiosis II).ġ. Download scientific diagram Average root length, mitosis phases (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) and MI according to treatment dose and. These four daughter cells are only half as numerous as chromosomes of the parent cell-haploid. One cell divides up twice during meiosis to create four daughter cells. Those cells are our sex cells-male sperm, female eggs. View the animation below, then complete the quiz to test your knowledge of the concept.Meiosis is a mechanism in which a single cell divides twice to produce four cells that contain half of the original amount of genetic data. These three stages are necessary for reproduction: the genetic material must be copied, the genetic material must be spatially separated, and only then can cell division occur. Finally, cytokinesis, the actual production of two different cells occurs during telophase. Metaphase II: The paired chromosomes line up. The segregation of DNA into two identical genomes begins in prophase and is completed by the end of anaphase. Meiosis II Prophase II: It is visibly obvious that replication has not occurred. The copying of DNA occurs during the S phase. Reproduction occurs in steps at different times in the cell cycle. During interphase, cells are primarily involved with growth and maintenance during the G1 and G2 stages. Individual cells exhibit all of these properties as they go through the cell cycle. How Cells Divide How the Cell Cycle Works How is the cell cycle related to the primary functions of life? Living things have the following properties: they reproduce, they maintain themselves (homeostasis), and they grow. Biology, Eighth Edition (Raven) Chapter 10:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
